Introduction
RA disease, also known as rheumatoid arthritis, is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the joints, causing pain, inflammation, and reduced mobility. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments is crucial for managing the disease effectively. In this article, we explore various treatments and alternatives to help individuals improve their quality of life and manage rheumatoid arthritis symptoms.
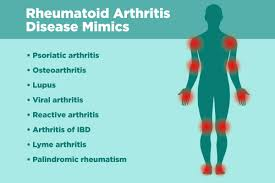
Understanding RA Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissue. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is caused by wear and tear, RA disease leads to inflammation that can damage joints over time.
Causes of RA Disease
The exact causes of RA disease are not fully understood, but several factors can increase the risk:
- Genetics: Family history of rheumatoid arthritis increases susceptibility.
- Immune System Dysfunction: Autoimmune response targets joint tissues.
- Environmental Factors: Smoking and certain infections may trigger RA.
- Hormonal Factors: Women are more likely to develop RA, suggesting hormones play a role.
Signs and Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Recognizing early signs of rheumatoid arthritis is essential for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Joint pain and tenderness
- Swelling and stiffness, especially in the morning
- Fatigue and weakness
- Fever in some cases
- Reduced range of motion
For a detailed overview of rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, visit Arthritis Foundation.
Diagnosis and Role of a Rheumatologist
Early diagnosis is key to preventing joint damage. Rheumatologists specialize in diagnosing and treating RA disease. Typical diagnostic methods include:
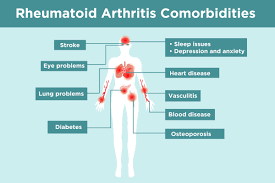
- Blood Tests: Detect rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-CCP antibodies.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound to identify joint damage.
- Physical Examination: Assessing joint swelling, tenderness, and mobility.
Prompt consultation with a rheumatologist can improve long-term outcomes.
Conventional Treatments for RA Disease
Managing RA disease typically requires a combination of medications and lifestyle modifications.
Medications
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Reduce pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroids: Provide rapid relief during flare-ups.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Slow disease progression.
- Biologics: Target specific immune responses for severe RA.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Regular low-impact exercise, such as swimming or yoga, can improve joint flexibility and reduce stiffness. Physical therapy can also help maintain mobility and strength.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Healthy Diet: Anti-inflammatory foods, rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
- Adequate Rest: Helps manage fatigue.
- Joint Protection: Using assistive devices to prevent strain.
For more information on RA treatments, visit Mayo Clinic.
Get Your Ultimate Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis Now!
Are you struggling with rheumatoid arthritis or worried about the early signs of RA? Don’t wait until the pain gets worse! Our comprehensive eBook, Rheumatoid Arthritis: Causes, Solutions, Treatments & Prevention, is your complete guide to understanding, managing symptoms, and preventing joint damage.
Inside this eBook, you’ll discover:
- Detailed explanations of rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and RA symptoms
- Proven strategies for rheumatoid arthritis treatment
- How to recognize early signs of rheumatoid arthritis before serious damage occurs
- Lifestyle tips, exercises, and diet plans for arthritis in fingers and other affected joints
- Expert advice for living a healthy, active life
Don’t let rheumatoid arthritis control your life! Take the first step towards relief and empowerment.
Click here to get your eBook now!
Why you need this eBook:
- Easy-to-understand language, perfect for anyone dealing
- Actionable solutions and preventive measures you can implement today
- Professional, science-backed guidance from experts in autoimmune health
Take control of your health—get your copy today and start managing like a pro!
Alternative and Complementary Approaches
Some individuals explore alternative treatments to complement conventional therapy.
Natural Remedies
- Supplements: Fish oil, turmeric, and vitamin D may help reduce inflammation.
- Herbal Treatments: Ginger, boswellia, and green tea have anti-inflammatory properties.
Mind-Body Techniques
- Meditation and Stress Management: Reduce stress-related flare-ups.
- Acupuncture: May alleviate joint pain in some patients.
Dietary Adjustments
- Anti-inflammatory Diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Processed foods, sugar, and excessive alcohol may worsen symptoms.
For research-based information, explore articles on NCBI.
Boost Your Joint Health with JointVive A Unique Solution for Comfort, Flexibility, and Mobility
Managing Symptoms and Improving Quality of Life
Living with RA disease involves proactive symptom management.
Pain Management Techniques
- Heat and cold therapy
- Massage therapy
- Over-the-counter pain relief
Joint Care
- Use ergonomic tools for daily activities
- Practice gentle stretching
- Avoid repetitive strain
Support Systems
- Join RA support groups
- Seek counseling for emotional well-being
- Educate family and caregivers about RA disease
Nutrition and Diet for Joint Health
A balanced diet plays a critical role in managing arthritis symptoms and maintaining joint health. Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods such as:
- Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel (rich in omega-3s)
- Leafy greens, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts
- Berries and citrus fruits high in antioxidants
- Whole grains like oatmeal and brown rice
Avoid processed foods, excessive sugar, and trans fats, which can worsen inflammation.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular movement helps maintain joint flexibility, muscle strength, and overall mobility. Recommended activities include:
- Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, or walking
- Strength training to support joint stability
- Stretching routines and yoga to improve flexibility
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting a new exercise regimen to prevent injury.
Mental Health and Coping Strategies
Chronic arthritis can affect emotional well-being. Effective coping strategies include:
- Mindfulness meditation to manage stress
- Counseling or therapy for emotional support
- Joining local or online support groups for shared experiences
Maintaining a positive mindset can reduce flare-ups and improve quality of life.
Advances in Medical Treatments
Ongoing research has introduced new options for managing rheumatoid arthritis:
- Targeted biologic therapies that focus on specific immune pathways
- Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors to reduce inflammation
- Personalized treatment plans guided by genetic and biomarker testing
Staying informed about emerging treatments can help patients discuss the best options with their rheumatologist.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is RA disease?
A1: RA disease, or rheumatoid arthritis, is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks joints, causing pain, inflammation, and reduced mobility.
Q2: What are the early signs of rheumatoid arthritis?
A2: Early signs include joint stiffness, swelling, fatigue, tenderness, and reduced range of motion.
Q3: How is RA disease diagnosed?
A3: Diagnosis involves blood tests, imaging studies, and a physical exam by a rheumatologist.
Q4: Are there natural treatments for RA disease?
A4: Yes, supplements like fish oil, turmeric, herbal treatments, mind-body techniques, and dietary adjustments can complement conventional therapy.
Q5: Can lifestyle changes help manage RA symptoms?
A5: Absolutely. Exercise, joint protection, proper rest, and a healthy diet can improve quality of life and reduce symptom severity.
Conclusion
RA disease is a chronic and potentially debilitating condition, but early diagnosis, proper treatment, and lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve quality of life. Understanding rheumatoid arthritis, its causes, signs, symptoms, and treatment options empowers patients to manage their condition effectively. Combining conventional treatments with alternative approaches and ongoing support from healthcare professionals and support systems ensures a comprehensive strategy to tackle RA disease.
SEE ALSO: RA: Early Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis
SEE ALSO: Rheumatoid Arthritis – E-book
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace the advice of a healthcare professional. Consult a doctor or nutritionist before starting any supplementation. Some links in the text are affiliate links, which means we may receive a commission if you make a purchase. This does not impact the price for you and helps us continue to bring you quality content.


Um comentário em “RA Disease: Treatments and Alternatives”