Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and potential joint damage. Recognizing the early signs of rheumatoid arthritis is crucial for timely intervention and effective management. This comprehensive guide delves into the various symptoms associated with RA, including common and unusual signs, progression stages, and available treatments.
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium—the lining of the membranes that surround the joints. This leads to inflammation that can cause joint damage and deformities over time. RA typically affects joints on both sides of the body, such as wrists, knees, and fingers.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis

1. Joint Pain and Swelling
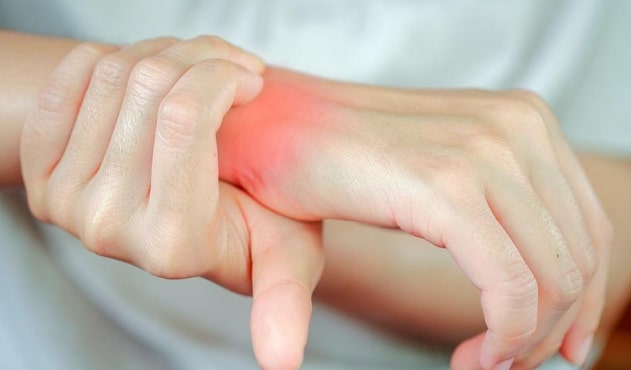
One of the hallmark signs of RA is joint pain and swelling, particularly in the small joints of the hands and feet. This pain is often accompanied by warmth and tenderness in the affected areas.
2. Morning Stiffness
Individuals with RA often experience stiffness in the joints upon waking, which can last for more than an hour. This stiffness is more pronounced in the morning and after periods of inactivity.
3. Fatigue
Persistent fatigue is a common symptom of RA, often preceding joint symptoms. This fatigue is not relieved by rest and can significantly impact daily activities.
4. Symmetrical Joint Involvement
RA typically affects joints on both sides of the body equally. For instance, if one knee is affected, the other knee is likely to be affected as well.
Early Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Recognizing early signs can lead to prompt diagnosis and treatment, potentially preventing severe joint damage.
1. Subtle Joint Discomfort
Mild discomfort in joints, especially after periods of rest, can be an early indicator of RA. This discomfort may be mistaken for general aches but can progress to more severe symptoms if left unaddressed.
2. Decreased Range of Motion
As inflammation sets in, individuals may notice a reduced range of motion in affected joints, making movements like gripping objects or bending fingers more challenging.
Unusual Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
RA can manifest in ways beyond joint-related symptoms.
1. Dry Eyes and Mouth
RA can affect moisture-producing glands, leading to dry eyes and mouth, a condition known as Sjögren’s syndrome.
2. Skin Rashes
Some individuals with RA develop skin rashes, including rheumatoid nodules—firm lumps under the skin near joints.
3. Lung Complications
RA can lead to lung issues, such as inflammation and scarring, resulting in symptoms like shortness of breath and chronic cough.
Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis in the Hands and Fingers
One of the most noticeable signs of rheumatoid arthritis appears in the hands and fingers. Swelling, stiffness, and tenderness often develop first in the small joints, such as those in the knuckles and wrists. Patients may notice difficulty gripping objects or performing daily tasks, such as buttoning a shirt or holding a pen. Early detection of these hand-related symptoms is crucial, as it can prevent long-term deformities and improve treatment outcomes.
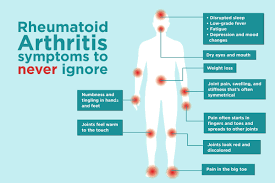
Systemic Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Beyond joint pain, signs of rheumatoid arthritis can manifest throughout the body. Fatigue, low-grade fever, and general malaise are common systemic symptoms. Some patients may experience loss of appetite or weight changes. Recognizing these systemic signs, in addition to joint-specific symptoms, allows for a more comprehensive diagnosis and timely medical intervention.
Progressive Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis: When Symptoms Worsen
As rheumatoid arthritis progresses, signs of rheumatoid arthritis become more pronounced and may include joint deformities, nodules under the skin, and increased pain and swelling. Morning stiffness can last several hours, and mobility may become limited. Identifying these progressive signs early is essential for adjusting treatment plans, incorporating physical therapy, and preventing further joint damage.
Early Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis You Shouldn’t Ignore
Recognizing the early signs of rheumatoid arthritis can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. Symptoms like mild joint pain, morning stiffness lasting more than an hour, and subtle swelling in fingers or wrists are often overlooked. Early detection allows patients to start therapies sooner, potentially slowing disease progression. For a detailed overview.
Unusual Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
While joint pain and stiffness are common, some patients experience less obvious signs of rheumatoid arthritis. These can include dry eyes, skin rashes, or fatigue that seems unrelated to joint issues. Understanding these unusual symptoms is crucial for comprehensive diagnosis. For additional information, check the Arthritis Foundation’s overview on rheumatoid arthritis.
Stages of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Understanding the progression of RA can aid in early detection and management.
Stage 1: Early RA
In the initial stage, inflammation occurs in the synovium, leading to joint pain and stiffness. X-rays typically show no joint damage at this point.
Stage 2: Moderate RA
Persistent inflammation begins to damage cartilage and bone, leading to visible joint changes and increased pain.
Stage 3: Severe RA
At this stage, joint deformities and significant loss of function occur, often requiring surgical intervention.
Stage 4: End-Stage RA
The final stage involves complete joint destruction and disability, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience persistent joint pain, swelling, or stiffness, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent joint damage.
Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Diagnosing RA involves a combination of physical examinations, blood tests (such as rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP antibodies), and imaging studies like X-rays or MRIs to assess joint damage.
Get Your Ultimate Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis Now!
Are you struggling with rheumatoid arthritis or worried about the early signs of RA? Don’t wait until the pain gets worse! Our comprehensive eBook, Rheumatoid Arthritis: Causes, Solutions, Treatments & Prevention, is your complete guide to understanding RA, managing symptoms, and preventing joint damage.
Inside this eBook, you’ll discover:
- Detailed explanations of rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and RA symptoms
- Proven strategies for rheumatoid arthritis treatment
- How to recognize early signs of rheumatoid arthritis before serious damage occurs
- Lifestyle tips, exercises, and diet plans for arthritis in fingers and other affected joints
- Expert advice for living a healthy, active life with RA
Don’t let rheumatoid arthritis control your life! Take the first step towards relief and empowerment.
Click here to get your eBook now!
Why you need this eBook:
- Easy-to-understand language, perfect for anyone dealing with RA
- Actionable solutions and preventive measures you can implement today
- Professional, science-backed guidance from experts in autoimmune health
Take control of your health—get your copy today and start managing your RA like a pro!
Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Early Stages
In the initial phase of rheumatoid arthritis, many people experience subtle but important signs of rheumatoid arthritis, such as mild joint swelling, tenderness, and slight stiffness in the mornings. These early indicators are often mistaken for general aches or fatigue. Early diagnosis can significantly improve long-term outcomes by enabling timely treatment. For more detailed information.
How to Recognize When Rheumatoid Arthritis Is Getting Worse
As rheumatoid arthritis progresses, it’s essential to monitor signs of rheumatoid arthritis that indicate worsening disease. These include increased joint pain, swelling, deformities, and reduced mobility. Patients may also experience more severe fatigue and systemic symptoms. Recognizing these changes early allows for adjustments in treatment plans, potentially preventing further joint damage. For expert guidance.
Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis
While there’s no cure for RA, various treatments can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
1. Medications
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): These drugs slow disease progression and prevent joint damage.
- Biologic Agents: Target specific components of the immune system to reduce inflammation.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Help alleviate pain and inflammation.
2. Physical Therapy
Physical therapists can design exercise programs to improve joint function and reduce stiffness.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding smoking can help manage RA symptoms.
Preventing Rheumatoid Arthritis
While RA cannot be entirely prevented, certain lifestyle choices may reduce the risk:
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for developing RA.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids may help reduce inflammation.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help maintain joint function and overall health.
Joint Health with JointVive
A Unique Solution for Comfort, Flexibility, and Mobility
For those looking for extra support in managing joint discomfort and maintaining mobility, JointVive can be a game-changer. Unlike anything else on the market, JointVive is crafted from a unique blend of rare, hard-to-source ingredients designed to help support joint comfort, flexibility, and overall mobility. Combined with proper lifestyle habits and RA management strategies, JointVive may provide the additional boost your joints need to stay active and pain-free. Don’t wait—take control of your joint health today! Click here to get JointVive now and start feeling the difference.
Early detection in fingers allows for prompt treatment and prevents permanent deformities.
FAQ
Q1: Can rheumatoid arthritis affect organs other than joints?
A1: Yes, RA can affect organs such as the lungs, heart, eyes, and skin, leading to complications like lung disease and eye inflammation.
Q2: Is rheumatoid arthritis hereditary?
A2: Genetics play a role in RA risk, but environmental factors also contribute. Having a family member with RA increases the risk.
Q3: Can children develop rheumatoid arthritis?
A3: Yes, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) affects children and can lead to growth problems and joint deformities if not treated early.
Q4: How is rheumatoid arthritis different from osteoarthritis?
A4: RA is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the joints, while osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease due to wear and tear.
Q5: Can rheumatoid arthritis go into remission?
A5: With effective treatment, many individuals experience periods of remission where symptoms are minimal or absent.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs of rheumatoid arthritis early can lead to timely treatment and better management of the disease. If you experience symptoms like joint pain, swelling, or stiffness, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and appropriate care.
SEE ALSO: Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Treatments and Conditions
SEE ALSO: Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapies: A Complete Review
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace the advice of a healthcare professional. Consult a doctor or nutritionist before starting any supplementation. Some links in the text are affiliate links, which means we may receive a commission if you make a purchase. This does not impact the price for you and helps us continue to bring you quality content.

